Fabulous Info About Financial Income Statement Deferred Tax Expense Example Ipsas 7

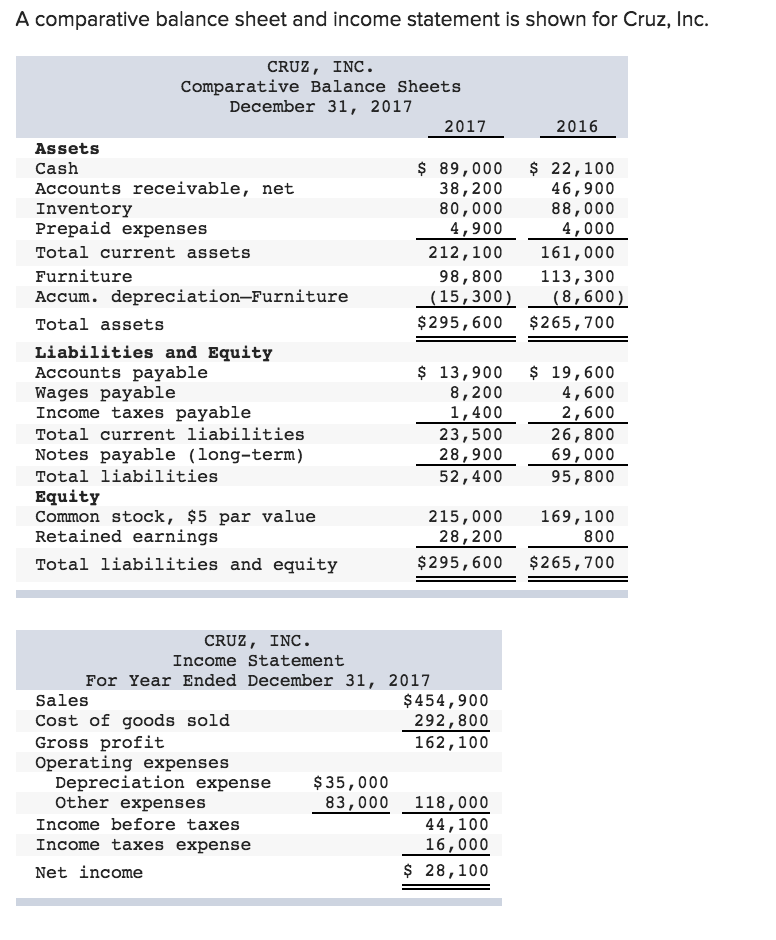
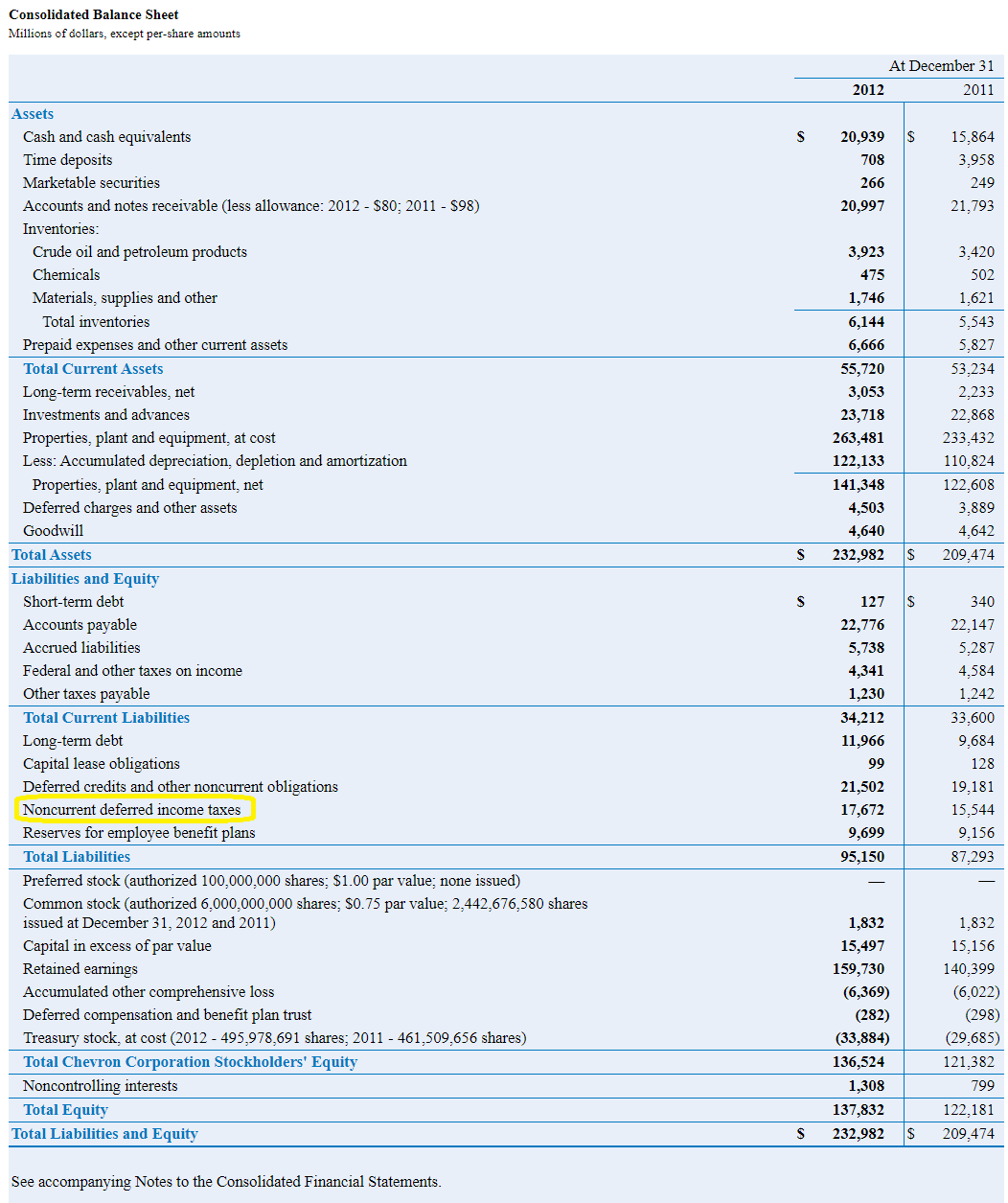
If the revenue for the period is $ 500,000, then the balance sheet of the company to the shareholders and the tax department will be:
Financial income statement deferred tax expense example. Nonetheless, they may require amortisation over a number of years for tax purposes. The deferred tax assets are the tax effects of expected future income tax benefits relating to: Simply put, deferred tax expenses are the reported income tax of a company or individual in the financial statement.
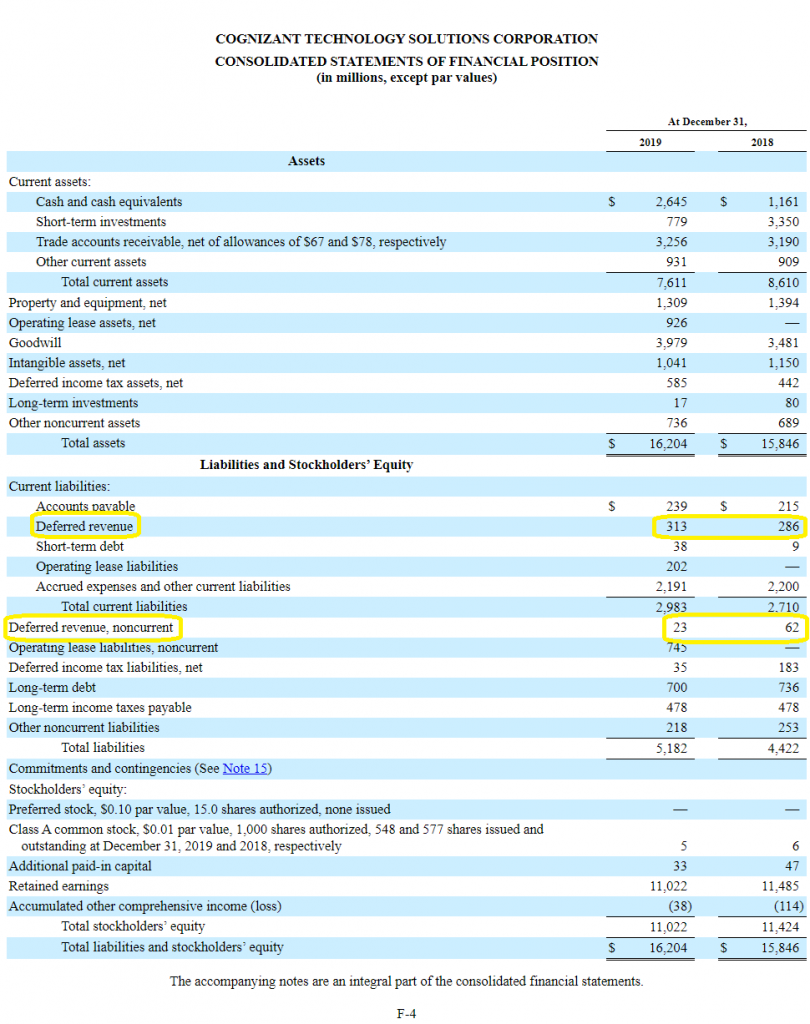
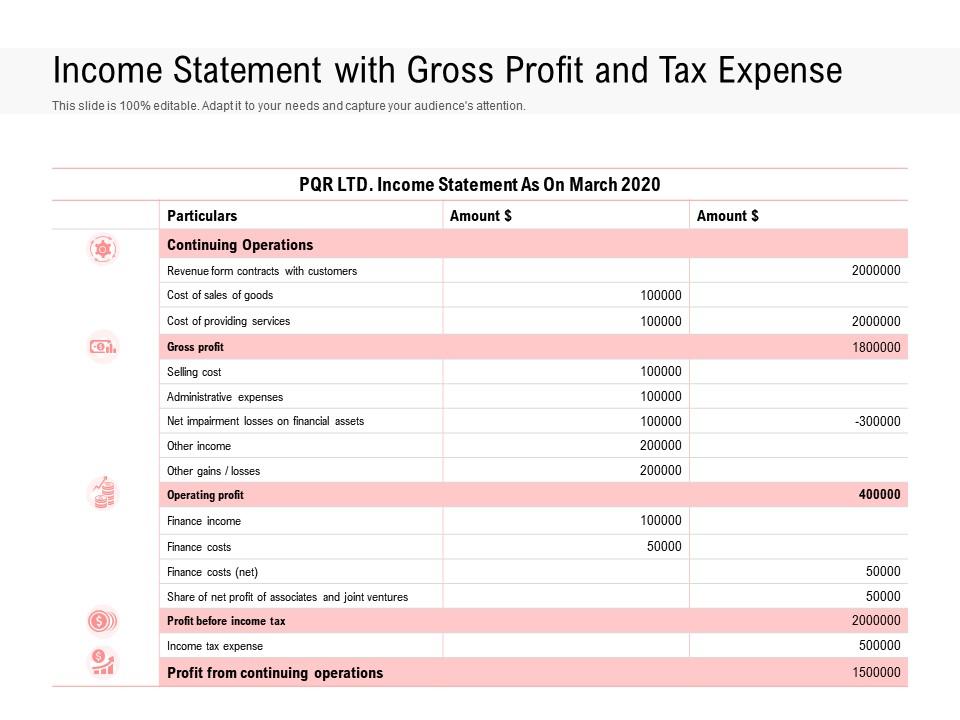
Total income tax expense or benefit for the year generally equals the sum of total income tax currently payable or refundable (i.e., the amount calculated in the income tax return) and the total deferred tax expense or benefit, adjusted for any unrecognized tax benefits. Top 4 examples of deferred revenue. Basic principles of deferred tax sunnie ltd prepares its financial statements to 31 march each year.
The timing of the cost recovery of the fixed asset may differ between the tax law for a particular jurisdiction and the applicable accounting rules, which can result in a deferred tax asset or. Basically their treatment as per income tax act differ from that under accounting standards/indian accounting standards. An example of this would be research costs.
Deferred tax expenses are particularly more useful in detecting earnings management for firms that avoid earnings decline. Income received in advance these are called timing differences. It can be different from the actual tax return resulting in liability or assets.
Generally, the income tax basis in a fixed asset is the purchase price less tax depreciation previously allowed under the applicable tax law. Example consider an electronics company xyz inc., which gives a warranty on the goods and assumes that the warranty repairs cost will go around 5% of the total revenue. On 31 dec 2017, the difference of depreciation and carrying value of truck between accounting base and tax base are as follow:
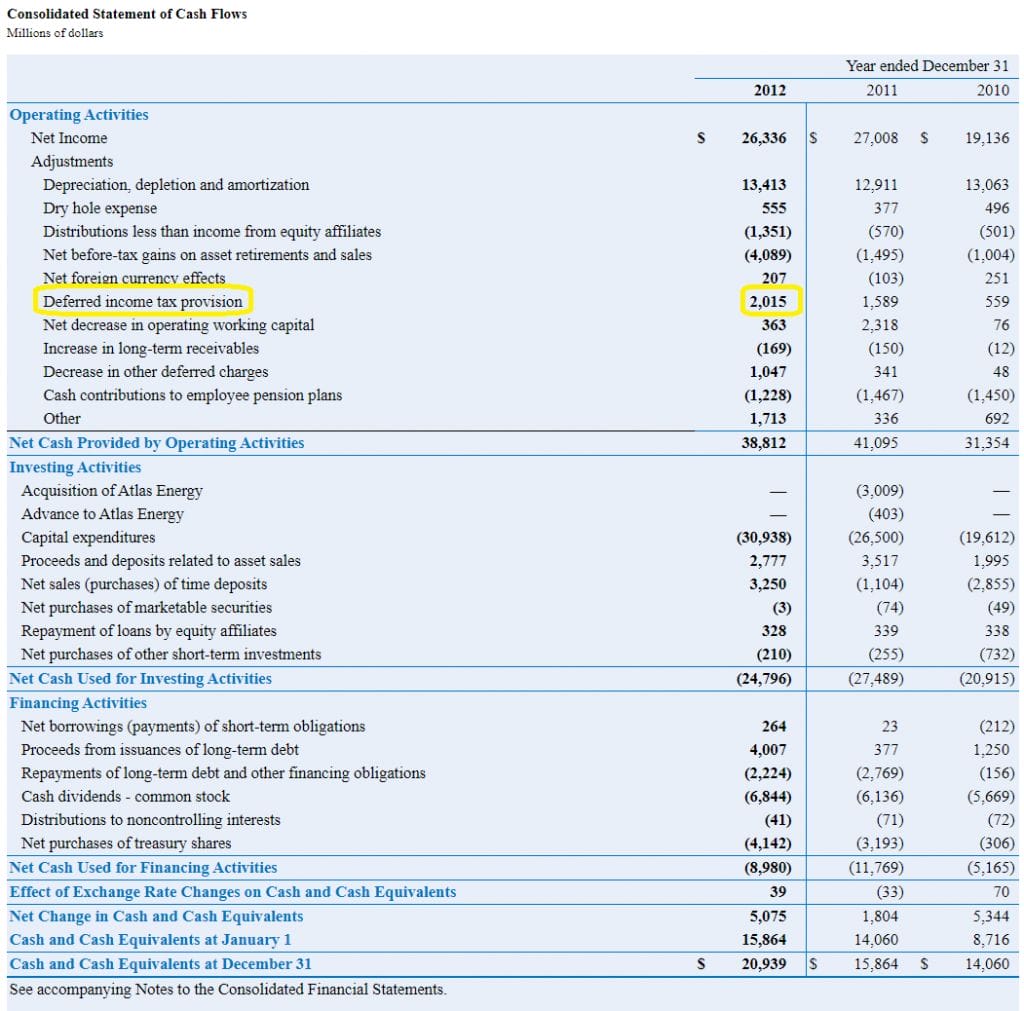
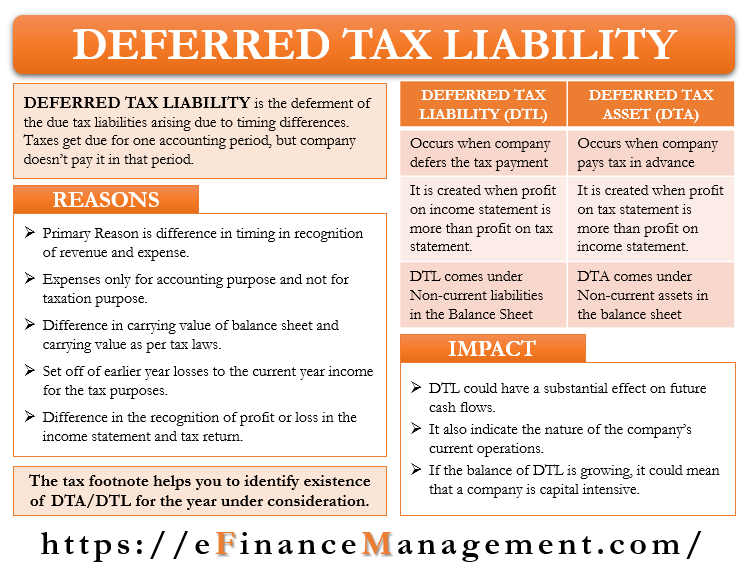
A deferred income tax is a liability recorded on a balance sheet resulting from a difference in income recognition between tax laws and the company’s accounting methods. Deferred tax expense. Depreciation = 40,000 *35% = 14,000
Depreciation on plants, properties and equipment 2. Unabsorbed depreciation or carry forward losses as per tax laws 3. These example financial statements are.
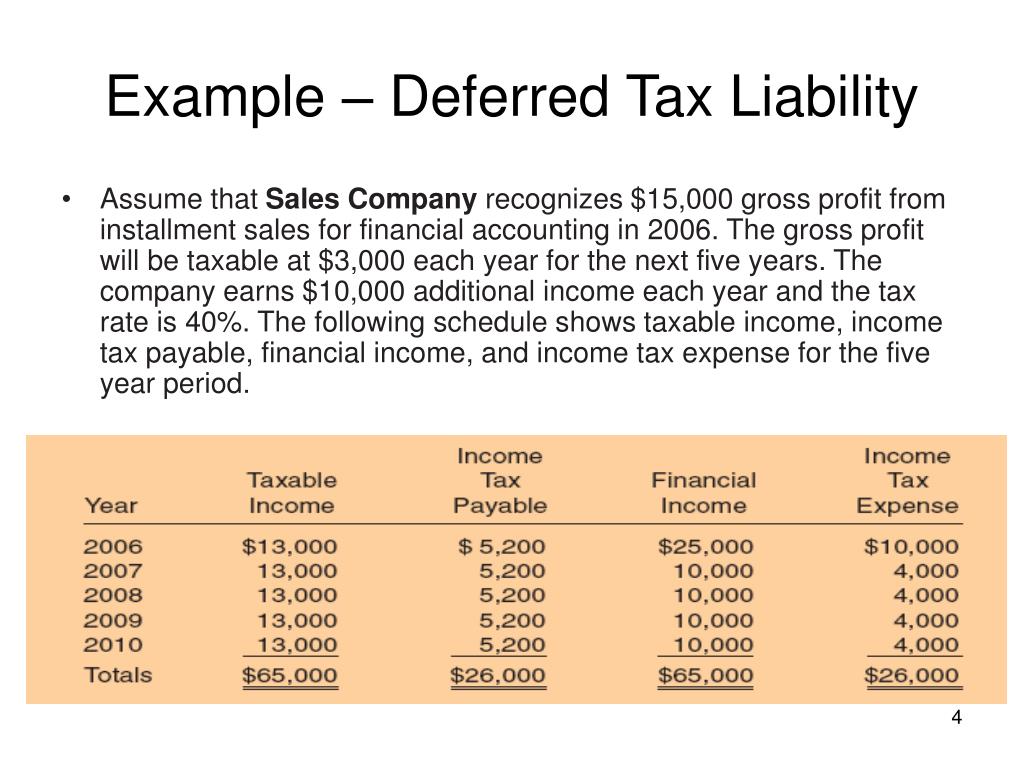
16 deferred tax assets and liabilities 68 17 inventories 70. The difference results in a surplus or deficit. Deferred tax expense may be negative which results in total tax expense being less than current income tax obligation.
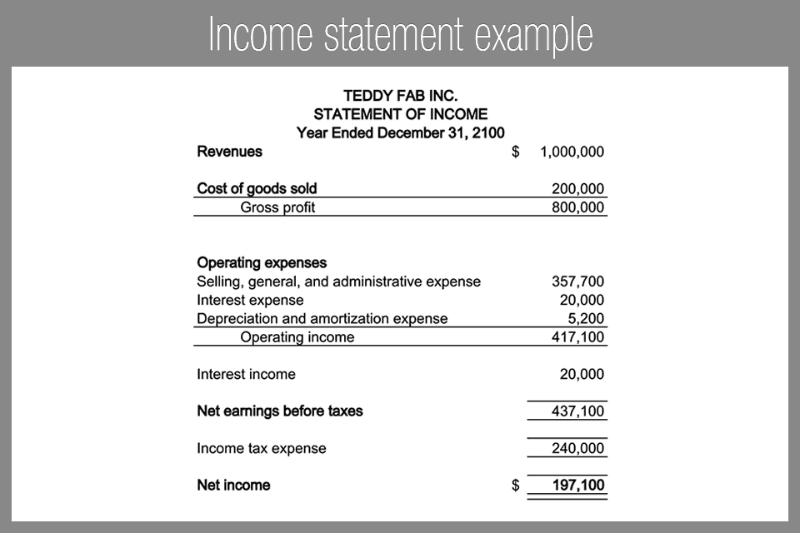
One straightforward example of a deferred tax asset is the carryover of losses. In practice, this is frequently presented on the face of the income statement. Tax bills once the deferred tax ‘turns into’ current tax.
According to ias 38, these costs are recognised as an expense as soon as they are incurred. It is the difference between income tax paid and income tax accrued. Deferred tax arises when there is a difference in the treatment of income, expenses, assets, and liabilities under the company’s accounting procedure and the tax provision.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/TermDefinitions_DeferredTax_V2-d5ae6ed922204f7eaa8bfb6b7b4b7f44.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/deferredincometax-v3-b8dc55e780ab4f47a0987161ece97060.png)





:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Deferred_Tax_Asset_Definition_Aug_2020-01-dab264b336b94f939b132c55c018f125.jpg)
