Unique Tips About Deferred Tax Expense Income Statement Vitol Financial Statements 2019

The basics deferred tax is accounted for in accordance with ias ® 12, income taxes.
Deferred tax expense income statement. It can be different from the actual tax return resulting in liability or assets. On the income statement, deferred tax. As deferred tax primarily arises due to timing differences between the accounting and taxation treatment.
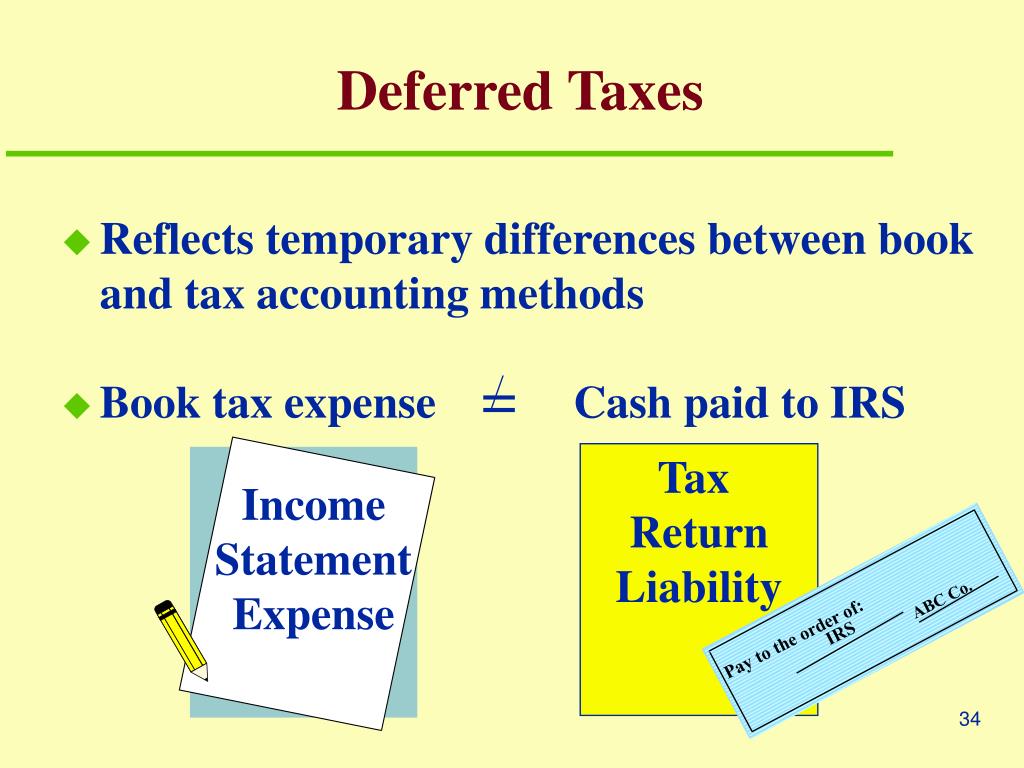
This guide summarises the approach to calculating a deferred tax balance, allocating the deferred tax charge or credit to the various components of the financial statements,. The dynamic on the income statement is more complex. A deferred tax liability (dtl) or deferred tax asset (dta) is created when there are temporary differences between book (ifrs, gaap) tax and actual income tax.
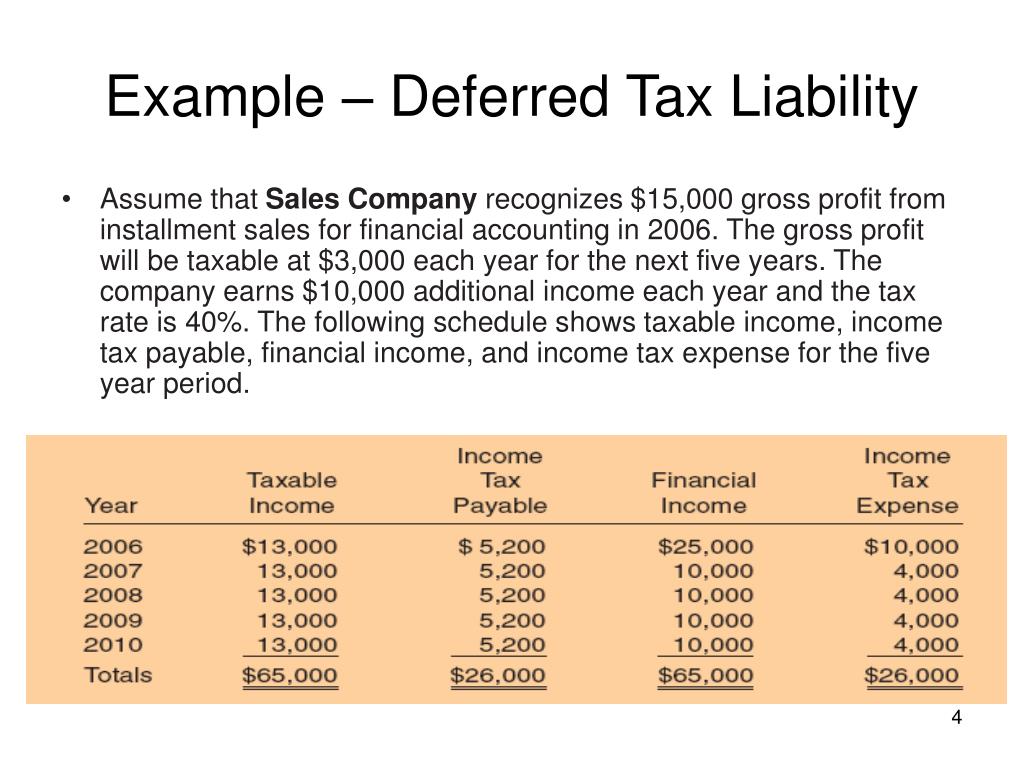
(ii) the amount of the deferred. This future deferred income tax expense (benefit) arises from temporary differences between book and tax value for certain items. The following formula can be used in the calculation of deferred taxes arising from unused tax losses or unused tax credits:
Asc 740 applies to all entities but only to. Deferred tax asset = unused tax. Deferred tax expense is the sum of any increase in deferred tax liability over a period minus an increase in deferred tax asset over the.
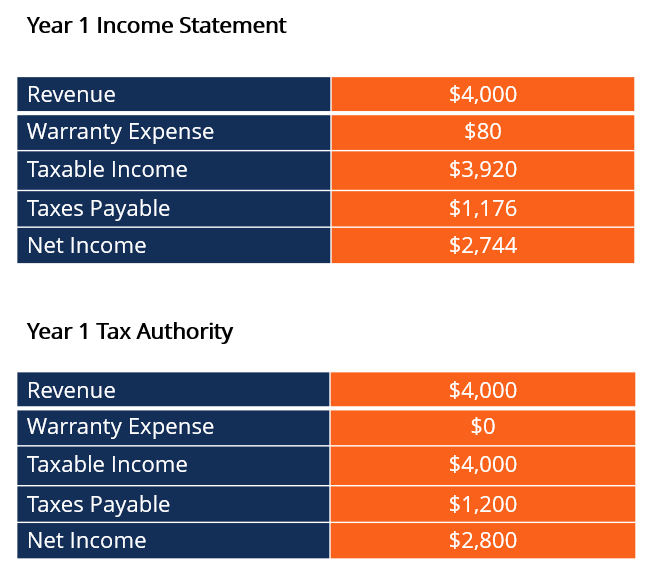
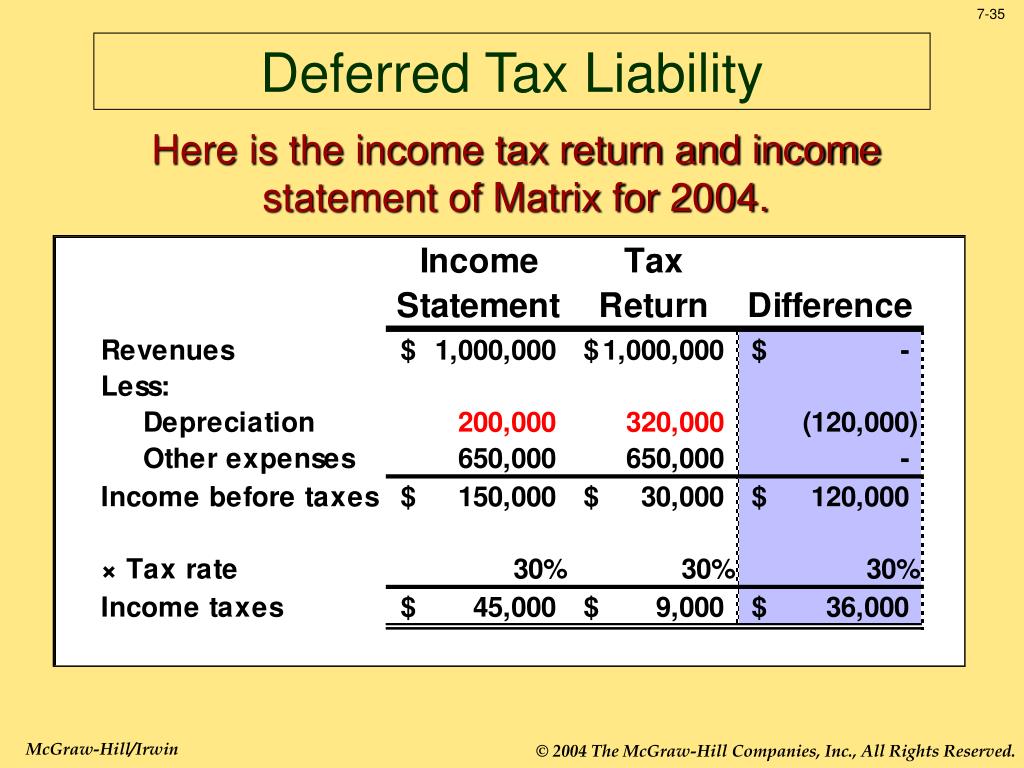
In the income statement, the provision for income taxes includes the impact of deferred income tax, which helps show how the deferred tax affects the company’s. For the year ended 31 march 2023, taxable profit is £150,000 and forecasts indicate that this level of profit is expected to continue for the next five years. The deferred tax expense is recorded because the tax year and the financial year are not the same.
The total tax expense in the ifrs income statement is composed of deferred income tax and current income tax. It is important to note that references to ‘income tax’ here are to tax on company profits or. Deferred tax expense affects the income statement, the balance sheet, and the cash flow statement of a business.
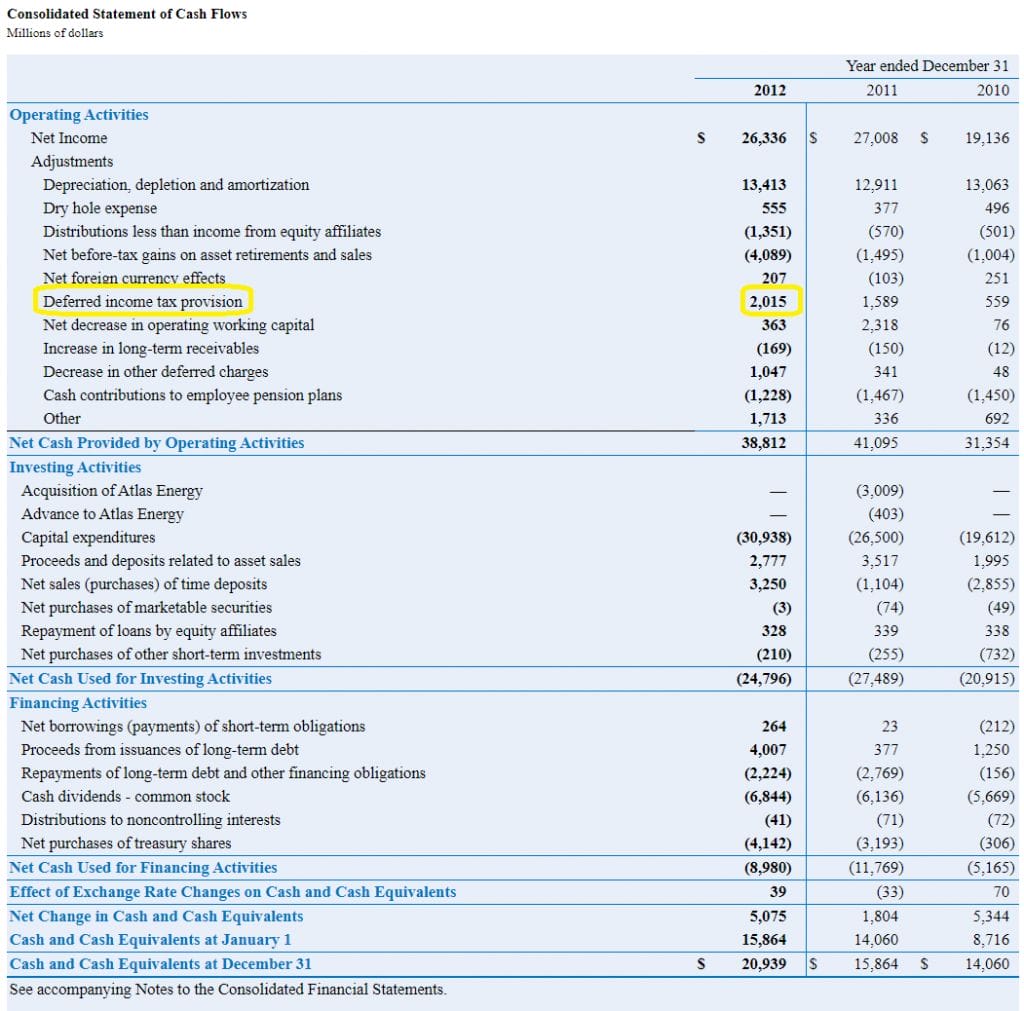
Total income tax expense or benefit for the year generally equals the sum of total income tax currently payable or refundable (i.e., the amount calculated in. The following chart illustrates when an accounting asset or liability (excluding income tax accounts) generates a corresponding deferred tax asset or liability: Deferred tax expense.
A deferred tax liability, or “dtl”, is created when the income tax expense recorded on a company’s income statement prepared under gaap accounting. Simply put, deferred tax expenses are the reported income tax of a company or individual in the financial statement.




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Deferred_Tax_Asset_Definition_Aug_2020-01-dab264b336b94f939b132c55c018f125.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/TermDefinitions_DeferredTax_V2-d5ae6ed922204f7eaa8bfb6b7b4b7f44.jpg)
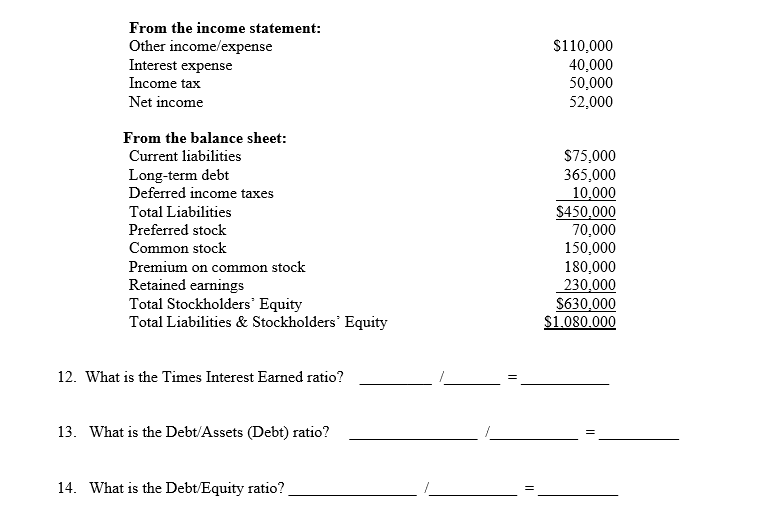
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/deferredincometax-v3-b8dc55e780ab4f47a0987161ece97060.png)