Painstaking Lessons Of Info About Negative Equity On Balance Sheet Which Financial Statement Is Reported As Of A Specific Date
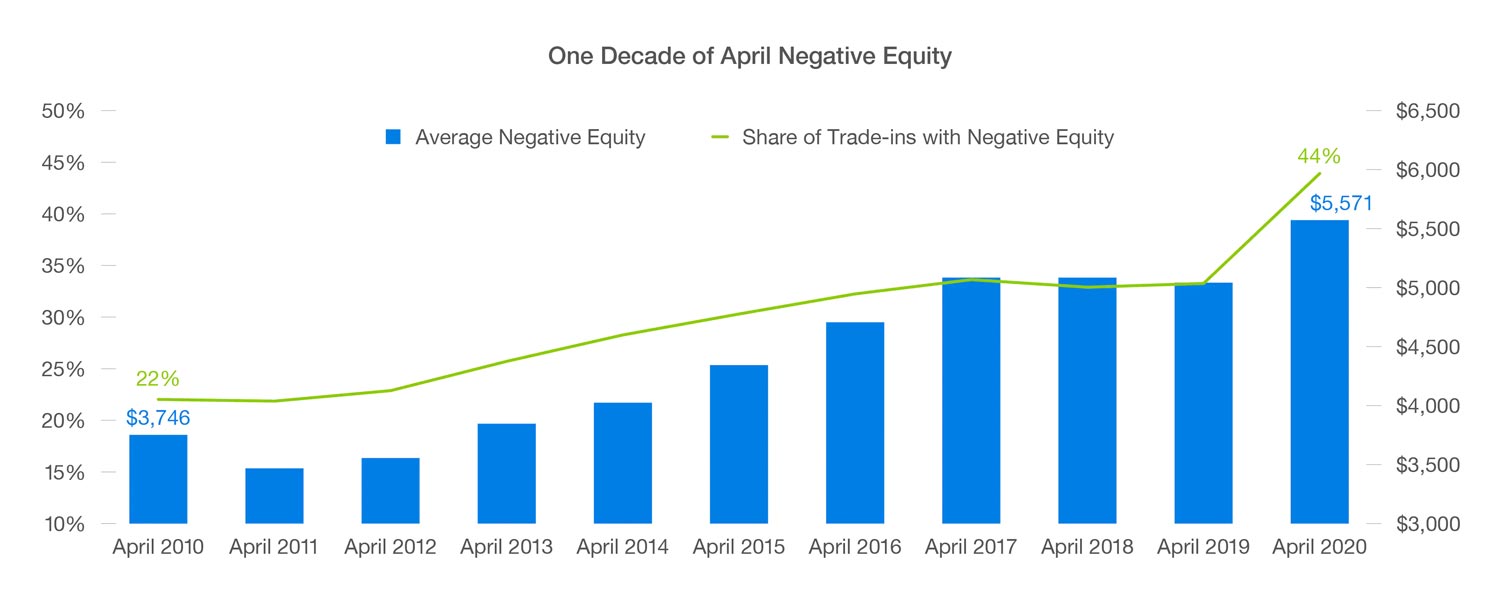
The overall worth of the company — or at least public opinion of that worth — may decrease.
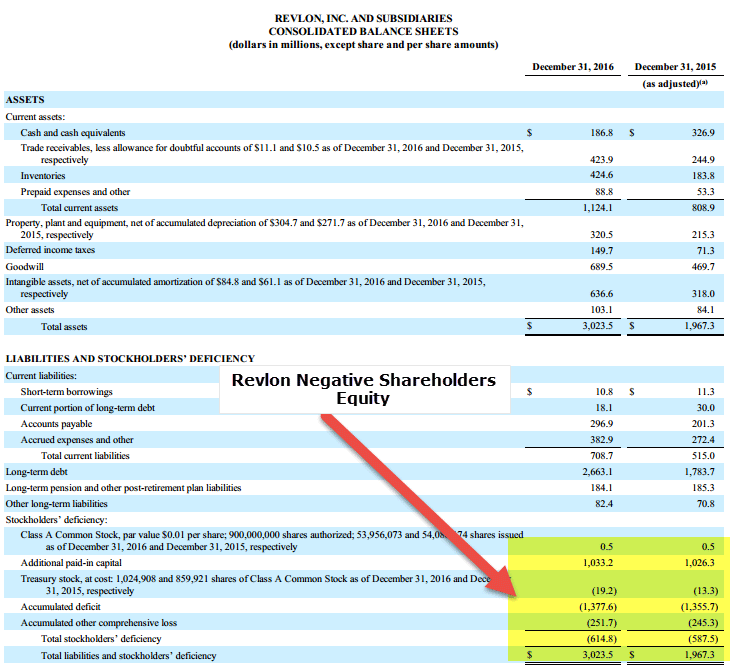
Negative equity on balance sheet. Reasons for negative shareholders' equity The negative numbers showing on the accounts indicate that there is a credit balance that made the company paid more than the expected amount. In addition, a reporting entity may combine an investment in common stock with.
This can be fixed by creating a journal entry to credit the accounts affected. Negative equity is reflected in the equity section of the balance sheet. In balance sheets, negative equity refers to the company's liability exceeding its assets.
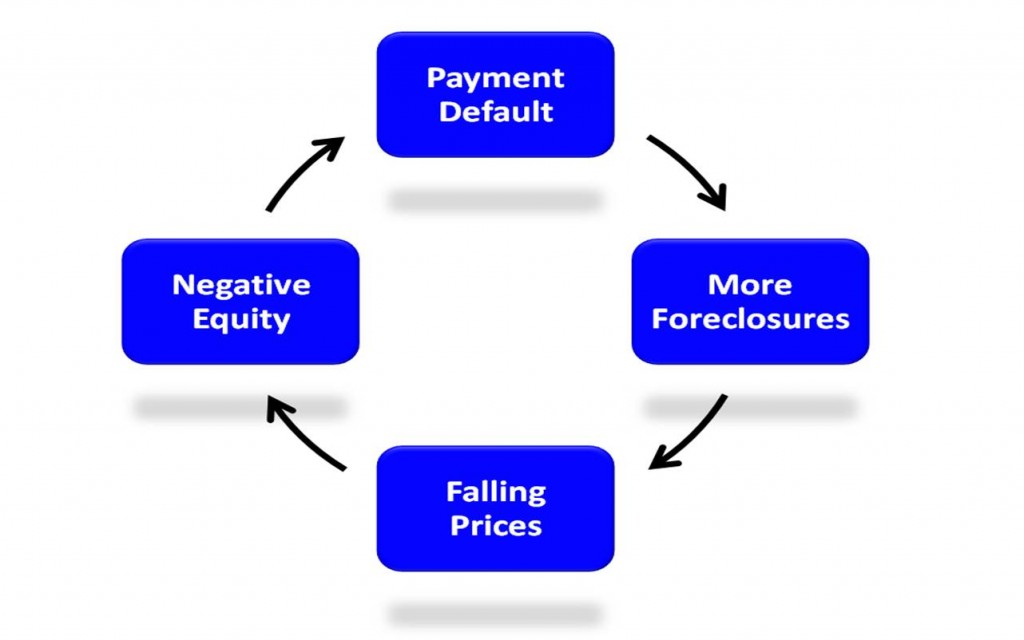
Negative equity erodes shareholders’ value and can lead to a decline in investor confidence. This study examines whether firms with debt contacts that contain more restrictive balance sheet covenants are more likely to conduct seasoned equity offerings. Negative equity on balance sheet occurs when a company’s debt is higher than its assets.
This way, the balance will be zeroed out. Raising capital via equity offerings allows the firm to increase net assets and thereby potentially avoid balance sheet covenant violations. It reflects the firm’s financial health, showing its assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity.
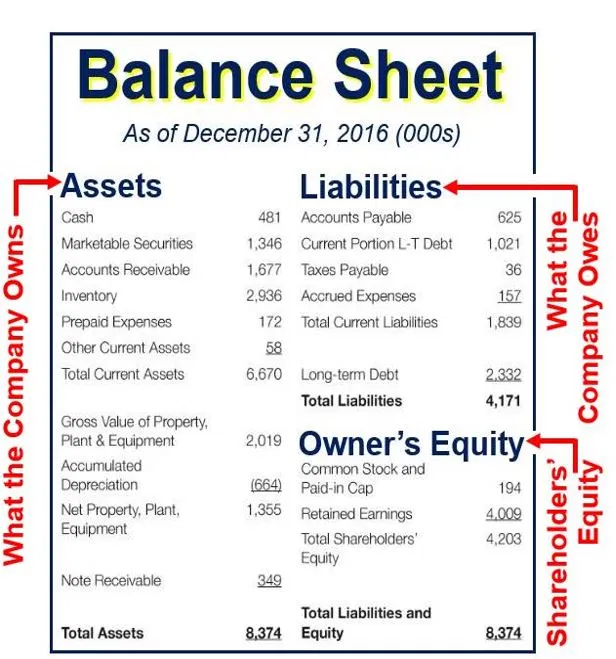
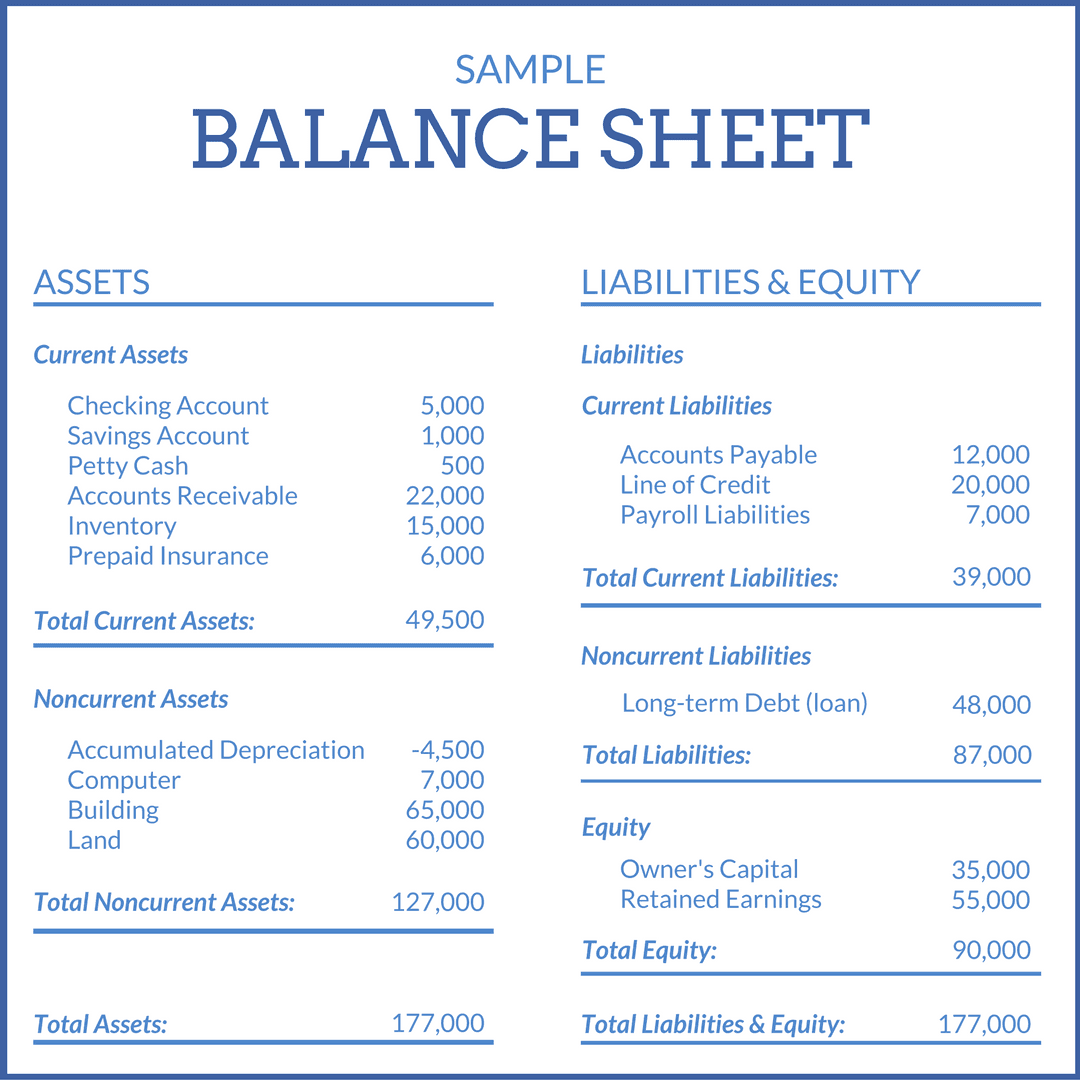
Reserves and surplus is reflected under shareholders funds in the balance sheet. On a company’s balance sheet, owners’ equity shows what the owners of the business (or shareholders) would have if the company paid off all its debt with its assets. Within the owners’ equity section, there may be several.
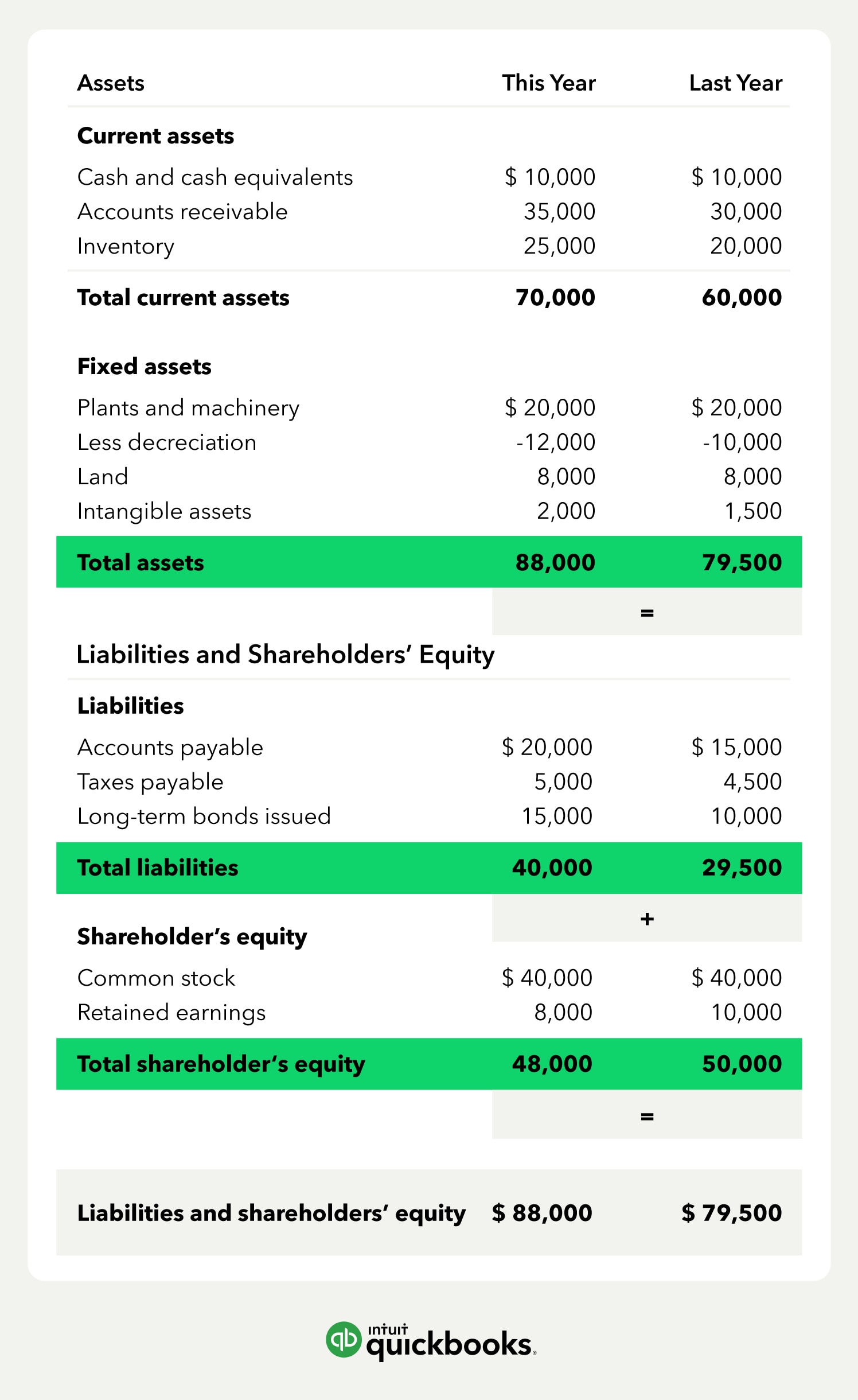
This financial statement is used both internally and externally to determine the so. At the bottom of the balance sheet, we can see that total liabilities and shareholders' equity are added together to come up with $324 billion which balances with apple's total assets. Before doing so, i recommend reaching out to your accountant so they.
With that said, here are two standard methods for identifying negative shareholders’ equity on financial statements: Extended periods of negative shareholders’ equity may have dire consequences. Instead of having a positive value, equity is shown as a negative figure, indicating that the company’s liabilities outweigh its assets.
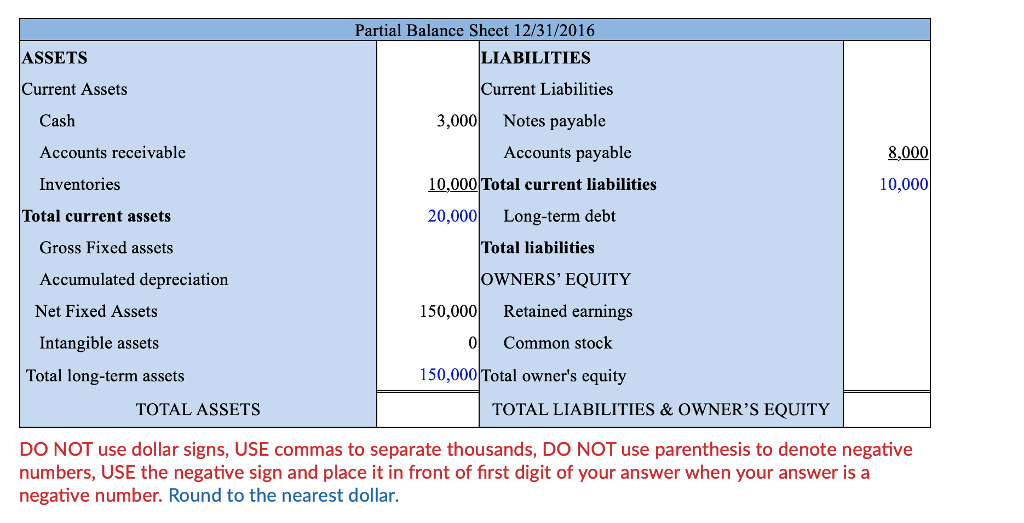
Multiple equity method investments can be aggregated for purposes of presentation on the balance sheet. A highly leveraged company can represent negative equity on its balance sheet as equity is valued at book values. The owner's equity at the end of the first year will be a negative $8,000.
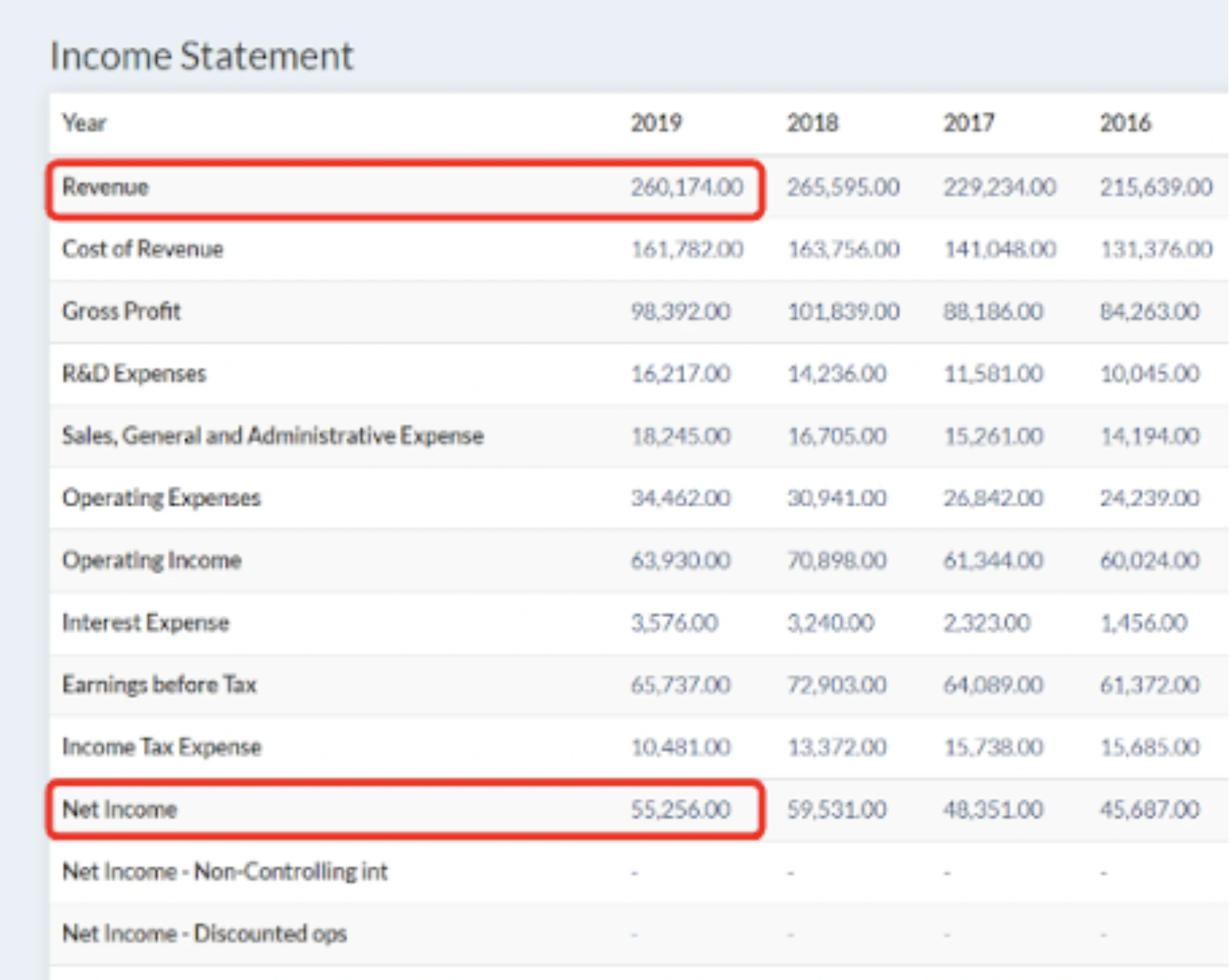
Negative equity on a balance sheet is a financial state where a company’s liabilities exceed its assets, signaling potential distress. Fundamental analysts use balance sheets to calculate financial ratios. If the current year's net income is reported as a separate line in the owner's equity or stockholders' equity sections of the balance sheet, a negative amount of net income must be reported.
The balance sheet adheres to an equation that equates assets with the sum of liabilities and shareholder equity. The balance sheet is based on the fundamental equation: Assets = liabilities + equity.





:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/phpdQXsCD-3c3af916d04a4afaade345b53094231c.png)


![Negative Equity The Latest Statistics [INFOGRAPHIC] Negativity](https://i.pinimg.com/originals/2c/ff/e6/2cffe6cf95e7eb9e19c7f431160ab5b4.jpg)